The L.A.W. of the Empire of Morocco
The Glossary serves as a comprehensive guide, providing links to every item within this book. It is designed to assist students in completing assignments more efficiently and in a more organized manner, especially when multitasking.
Mission Statement
The purpose of this Dictionary is to connect the historical timeline of the Moroccan Empire to the present day, in conjunction with the AMPAC Study Sessions. Inside, you will find a wealth of information, including:
-
Moroccan History: A detailed account of the Moroccan Empire's past.
-
Treaties: Important treaties that have shaped the Empire.
-
Key Definitions: Essential terms defined for better understanding.
-
Maps: Detailed maps of all Moroccan territories.
-
Foreign Moroccan Countries or States: Information on foreign states within the Moroccan Empire.
-
Internal Moroccan States' Declarations of Independence: Key declarations from internal states.
-
Constitutions: Constitutions of all jurisdictions within the Empire of Morocco.
-
Laws: Internal and external laws governing Moroccan states and foreign jurisdictions within the Empire.
-
AMPAC Study Sessions: Documents and definitions discussed in AMPAC Study Sessions.
Continuous Updates
The L.A.W. of the Empire of Morocco will be continuously updated to ensure that the information remains current and accurate.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
S |
|---|
Self-coupA self-coup, also called an autocoup (from Spanish autogolpe) or coup from the top, is a form of coup d'état in which a political leader, having come to power through legal means, stays in power illegally through the actions of themselves or their supporters.[1] The leader may dissolve or render powerless the national legislature and unlawfully assume extraordinary powers. Other measures may include annulling the constitution, suspending civil courts, and having the head of government assume dictatorial powers.[2][3] From 1946 to the beginning of 2021, an estimated 148 self-coup attempts took place, 110 in autocracies and 38 in democracies.[4] | |
Signatory Powers or Third StatesSignatory Powers or Third States parties to the multilateral Act of Algeciras of 1906 per intertemporal Law | |
Sovereign CitizensThe term “sovereign citizen” refers to an individual who does not agree with a particular law and will find any means of justifying his noncompliance with that law. An example of a sovereign citizen is someone who refuses to pay his income taxes, and then presents “evidence” as to why he should not have to pay them. Such “evidence” can come in the form of websites that support his ideology, or excerpts from Supreme Court decisions that he manipulates into justifying his point of view. To explore this concept, consider the following sovereign citizen definition. Definition of Sovereign CitizenNoun
Origin 1971 | |
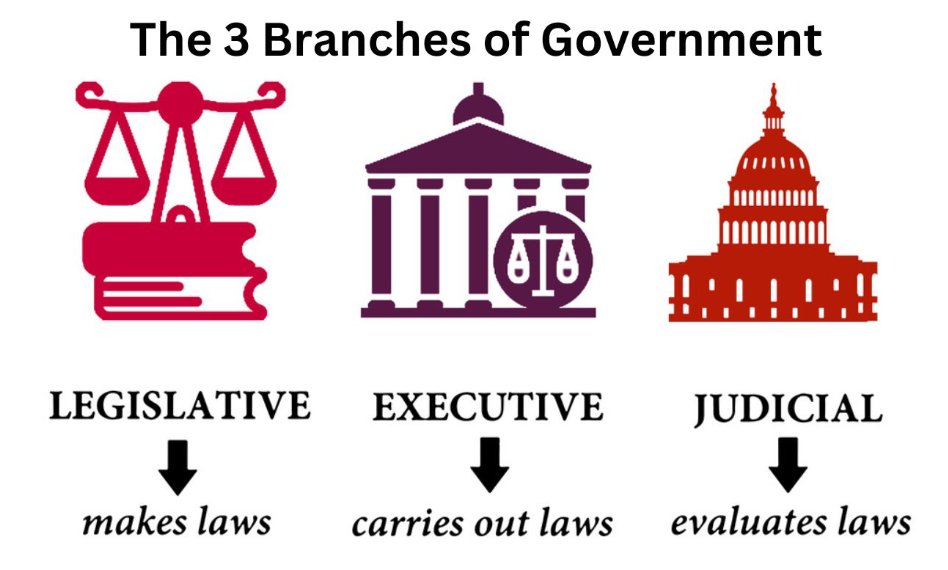
Speaker of The House (Moroccan Only)Chapters & Articles Relating to the Speaker of the HouseChapter V – House Members of the Legislative Branch
Chapter VI – Relations Between Government and the House
Chapter VII – Treaties and International Agreements
Chapter VIII – Constitutional Council
Chapter IX – Judicial Authority
Chapter XIII – Defender of Rights
Chapter XV – Transitional Provisions for Trust Territories
Speaker of the House – Practical Duties & Procedures Guide(Empire of Morocco Constitution – Operational Reference)Chapter V – House Members of the Legislative BranchArticle 27 – Composition and Leadership of the HouseRole/Function: Preside over the House, represent it internally and externally, and ensure constitutional procedures are followed. Operational Tasks:
Article 28 – Terms and EligibilityRole/Function: Ensure Members meet eligibility requirements and terms are respected. Operational Tasks:
Article 29 – Parliamentary ImmunityRole/Function: Safeguard Members’ privileges and ensure due process in legal matters. Operational Tasks:
Article 30 – Voting and SessionsRole/Function: Manage voting procedures and session scheduling. Operational Tasks:
Article 31 – Extraordinary SessionsRole/Function: Coordinate extraordinary sessions and ensure agendas are followed. Operational Tasks:
Article 32 – Opening/Closing by SultanRole/Function: Liaise with the Sultan’s office for ceremonial openings/closings. Operational Tasks:
Article 33 – Government Access to the HouseRole/Function: Facilitate government participation in House proceedings. Operational Tasks:
Article 34 – Term of the SpeakerRole/Function: Provide stable leadership over a seven‑year renewable term. Operational Tasks:
Article 35 – Public SittingsRole/Function: Ensure transparency and publication of proceedings. Operational Tasks:
Chapter VI – Relations Between Government and the HouseArticle 43(5) – Private Member’s BillsRole/Function: Submit bills to the Attorney General for opinion before committee review. Operational Tasks:
Article 45 – Inadmissibility RulingsRole/Function: Ensure legislative proposals meet constitutional and procedural requirements. Operational Tasks:
Article 49(2) – Legislative MediationRole/Function: Resolve legislative deadlocks. Operational Tasks:
Chapter VII – Treaties and International AgreementsArticle 64 – Constitutional Review of TreatiesRole/Function: Refer treaties to the Constitutional Council if constitutional conflict is suspected. Operational Tasks:
Chapter VIII – Constitutional CouncilArticle 66 – AppointmentsRole/Function: Appoint 13 members to the Constitutional Council. Operational Tasks:
Article 69 – Election OversightRole/Function: Ensure legitimacy of Speaker elections. Operational Tasks:
Article 71(2) – Referral of ActsRole/Function: Refer Acts to the Constitutional Council before promulgation. Operational Tasks:
Chapter IX – Judicial AuthorityArticle 77(1–2) – High Council of the Judiciary AppointmentsRole/Function: Appoint two members to the High Council of the Judiciary. Operational Tasks:
Chapter XIII – Defender of RightsArticle 88(2) – Appointment of Defender of Rights PresidentRole/Function: Appoint the President of the Defender of Rights. Operational Tasks:
Chapter XV – Transitional Provisions for Trust TerritoriesArticle 98(6) – Recognition of Trust TerritoriesRole/Function: Participate in formal recognition of new Moorish States. Operational Tasks:
Don’t ForgetThe Speaker’s office is both guardian of legislative integrity and manager of parliamentary operations. Beyond presiding over debates, the Speaker safeguards constitutional compliance, manages high‑level appointments, and acts as a bridge between the House, the Government, and the Sultan.Speaker of the House – Constitutional Mandate(Empire of Morocco Constitution – Consolidated Provisions) Chapter V – House Members of the Legislative BranchArticle 27 – Composition and Leadership of the House
Article 28 – Terms and Eligibility
Article 29 – Parliamentary Immunity
Article 30 – Voting and Sessions
Article 31 – Extraordinary Sessions
Article 32 – Opening/Closing by Sultan
Article 33 – Government Access to the House
Article 34 – Term of the Speaker
Article 35 – Public Sittings
Chapter VI – Relations Between Government and the HouseArticle 43(5) – Private Member’s Bills
Article 45 – Inadmissibility Rulings
Article 49(2) – Legislative Mediation
Chapter VII – Treaties and International AgreementsArticle 64 – Constitutional Review of Treaties
Chapter VIII – Constitutional CouncilArticle 66 – Appointments
Article 69 – Election Oversight
Article 71(2) – Referral of Acts
Chapter IX – Judicial AuthorityArticle 77(1–2) – High Council of the Judiciary Appointments
Chapter XIII – Defender of RightsArticle 88(2) – Appointment of Defender of Rights President
Chapter XV – Transitional Provisions for Trust TerritoriesArticle 98(6) – Recognition of Trust Territories
TL;DR – Core MandateThe Speaker of the House is the presiding officer and constitutional guardian of the legislative branch, with powers spanning:
| |
Study Session: ResourcesInternational Convention for the Suppression of the Traffic in Women of Full Age 1933 "The sole function of this resource is to provide a straightforward list of items that can be seamlessly copied and pasted into the search field. It is designed purely for convenience, ensuring users have quick access to preformatted, searchable terms without the need for additional editing or formatting. By simplifying the process, this tool saves time and effort, serving as an efficient reference for study sessions or research needs. These items can be found here in the L.A.W. book by clicking the first letter of the item and searching the list." | |
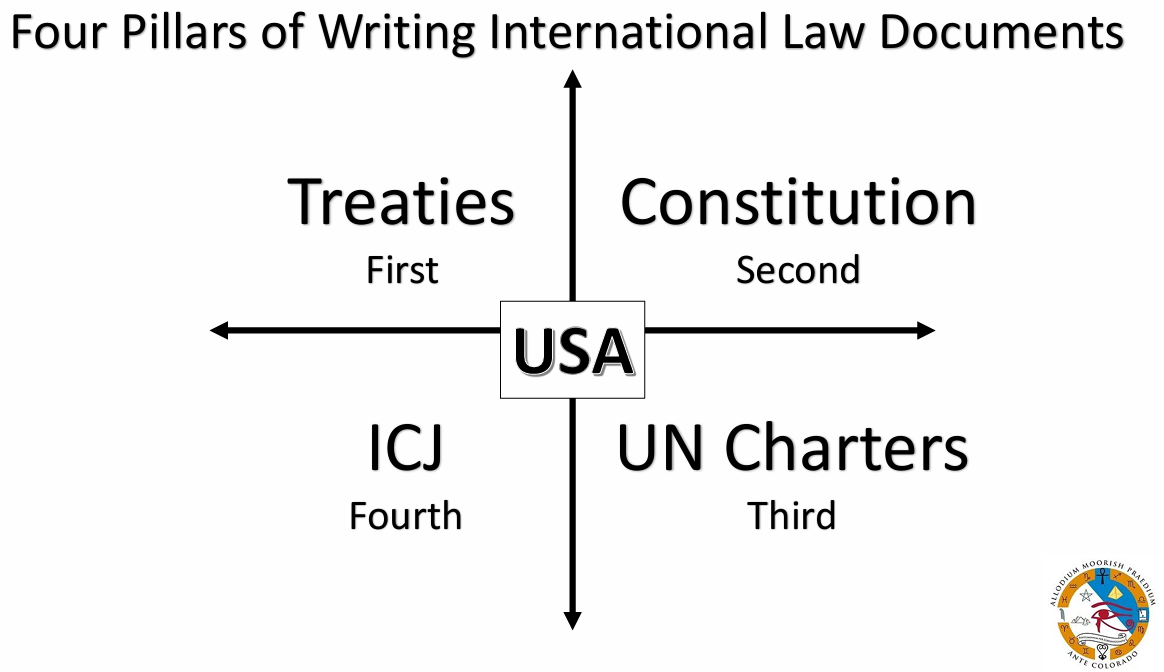
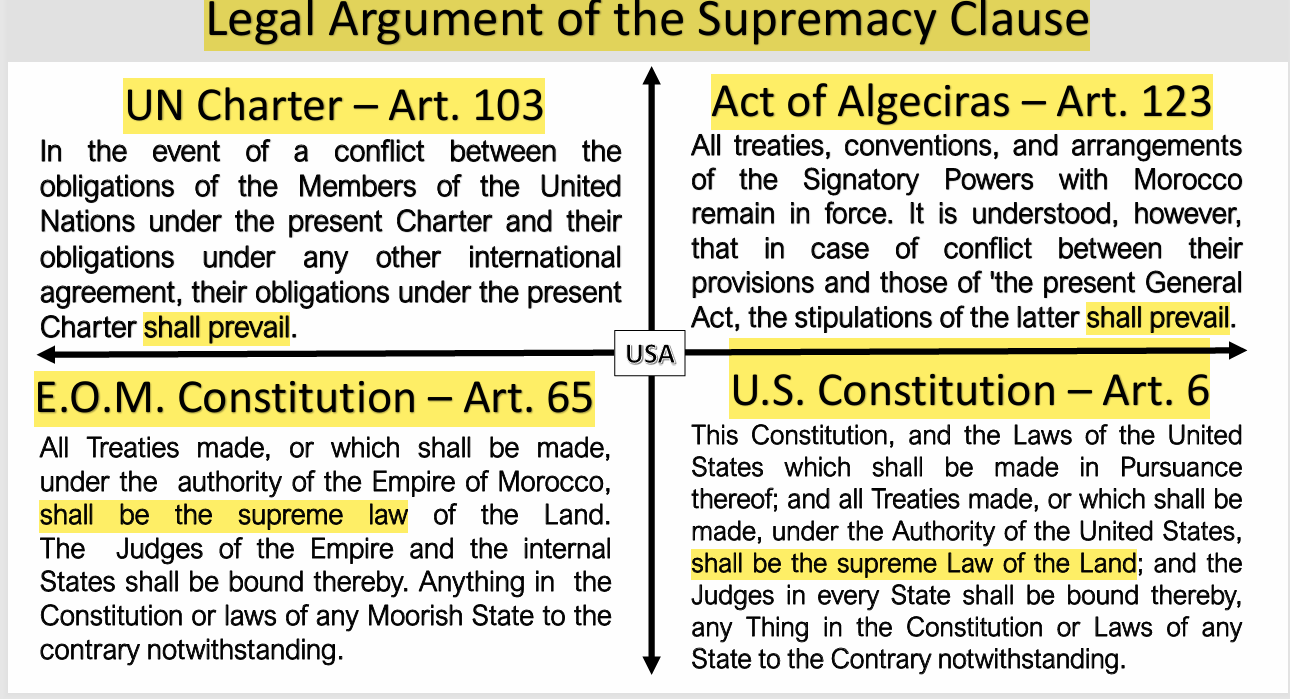
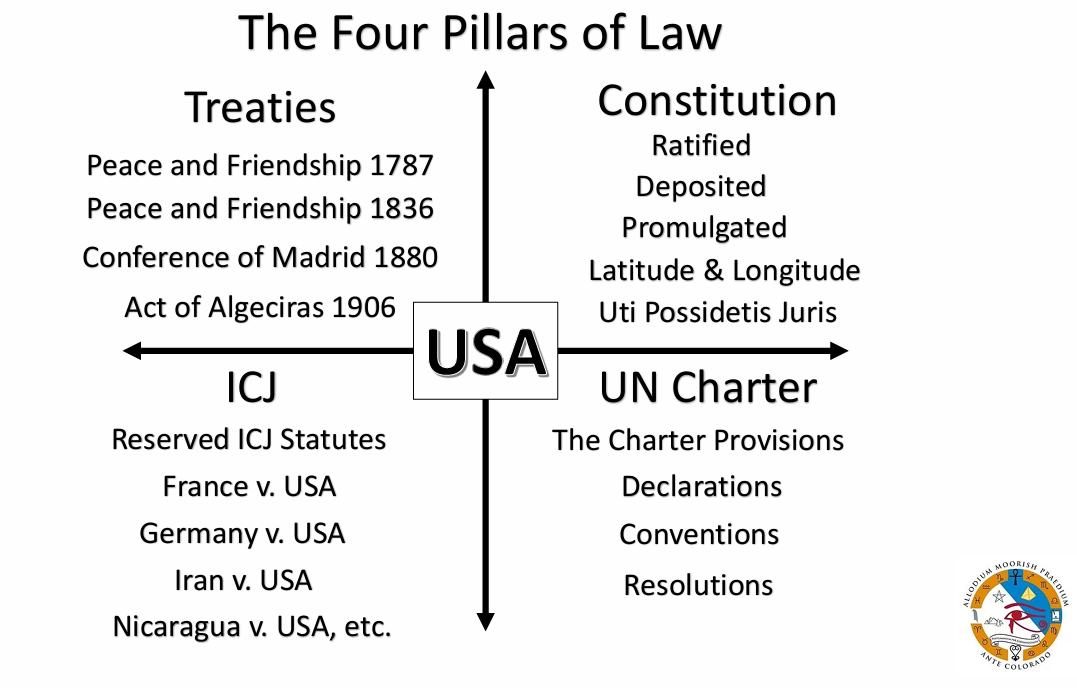
Supremacy ClauseSupremacy ClauseThe Supremacy Clause refers to the foundational principle that, in general, federal law takes precedence over any conflicting state law. Established under Article VI, Paragraph 2 of the U.S. Constitution, the Supremacy Clause enables the federal government to enforce treaties, create a central bank, and enact legislation without interference from the states. It does not, however, allow the federal government to review or veto state laws before they take effect. The Supremacy Clause underpins the broader doctrine of preemption, where if laws are in conflict, the law of a higher authority can preempt the law of a lower authority if the superiority of the former is stated expressly or implied. Traditionally, when it is not indicated, federal law does not preempt state law in areas traditionally regulated by states, unless Congress’s intent to preempt is clear. In areas where the federal government has historically significant regulatory involvement, preemption is less likely to apply. Today, disputes usually involve statutory interpretation rather than its scope of application. Purpose & IntentThe Purpose and intent of the Supremacy Clause is to overrule, Supersede, or preempt any inferior entity, law, or procedure without prejudice to the subject matter jurisdiction of the competent court of Law. See also: Constitutional Clauses Supremacy ClauseQuestion: What is the purpose and intent of the supremacy clause (i.e., supreme law), supremacy language, or procedure? Answer: Supremacy Clause (i.e., supreme law) supersedes, overrule procedures. Moors) Legal Argument of the Supremacy Clause 2. Act of Algeciras (1906) Art. 123 and last. All treaties, conventions, and arrangements of the Signatory Powers with Morocco remain in force. It is understood, however, that in case of conflict between their provisions and those of the present General Act, the stipulations of the latter shall prevail. 3. Empire of Morocco Constitution 2024 ARTICLE 65. 4. United States Constitution Article. VI. Clause 2. All Debts contracted and Engagements entered into, before the Adoption of this Constitution, shall be as valid against the United States under this Constitution, as under the Confederation This Constitution, and the Laws of the United States which shall be made in Pursuance thereof; and all Treaties made, or which shall be made, under the Authority of the United States, shall be the supreme Law of the Land; and the Judges in every State shall be bound thereby, any Thing in the Constitution or Laws of any State to the Contrary notwithstanding. The Senators and Representatives before mentioned, and the Members of the several State Legislatures, and all executive and judicial Officers, both of the United States and of the several States, shall be bound by Oath or Affirmation, to support this Constitution; but no religious Test shall ever be required as a Qualification to any Office or public Trust under the United States
Supremacy Clause refer to Study Session #163 | |
Synergysynergynounsyn·er·gy How to pronounce synergy (audio)
pluralsynergies
2
: a mutually advantageous conjunction or compatibility of distinct business participants or elements (such as resources or efforts)
| |